
National Accreditation Board for Hospitals [NABH], a constituent board of Quality Council of India [QCI], have come up with standards for accrediting Hospitals with an aim to provide a framework for quality assurance and quality improvement. Intent of the standards is to provide information to patients about the level of healthcare an institution can or can not provide.
NABH standard definition covers 10 criteria groups – first five are patient centric and second five are organization centric.
Relevant ICT technologies/functionalities facilitating compliance to these standards are mentioned below grouped as per NABH criteria.
Access, Assessment and Continuity of Care (AAC) Criteria Group:
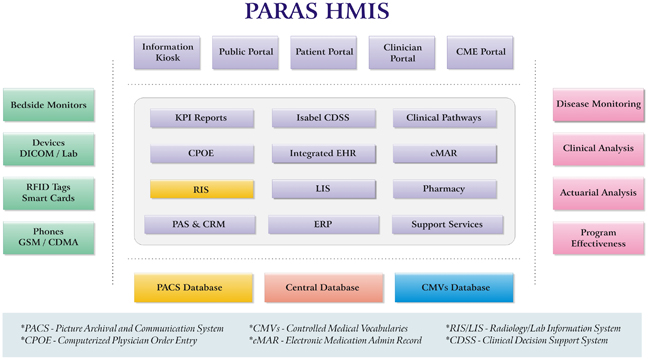
Standards for ‘Registration’, ‘Admission’, ‘Discharge’, ‘Transfer’ & ‘Referral’ processes are covered in this group and are properly taken care of using the Patient Administration System [PAS] module of an HMIS. This functionality forms one of the basic block of a modern Hospital Management Information System [diagram 1].

[Diagram 1: HMIS Functionality Stack]
Standard Clinical Assessment, including alerts for Allergy, ADR & Critical Problems are greatly assisted by ICT usage. Life critical information related to Allergy or ADR once captured, is available across all the points of care in a hospital, thereby improving standards of care to great extent and also preventing life threatening mistakes.
Standardised Lab & Imaging services are covered through Laboratory Information System [LIS] & Radiology Information System [RIS]. RIS systems, either stand alone or as a part of a modern HMIS, consist of a Picture Archival & Communication System [PACS] Server which is connected to different workstations [diagram 2].

Standards related to ‘Consent Recording/Archiving’ are an important constituent of this group. Using ICT not only situation specific consent forms can be printed [using templates saved in the application] and used but the signed forms can be scanned and saved in the application, making them available across time and space.
Care of Patients (COP)
By using specialty specific Clinical ‘Packs’, ICT ensures a standardized delivery of clinical care across all locations & departments of a Hospital. Using Clinical Process Guidelines [CPG] modern EHR systems provide a ‘workflow template’, using which Health Care Professionals traverse a pre charted path and thereby ensuring a standard model of care.
– An Approach Whitepaper by Dr Vinoy Singh


